Metropolitan Area Networks
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a relatively new type of network. In terms of its size, it is usually falls between a local area network and a wide area network, and typically covers an area of between five and fifty kilometres in diameter. A MAN can cover a group of corpporate offices or an entire city, and can be either privately or publicly owned. A MAN can support both data and voice communication, and does not contain switching elements, simplifying design. A standard has been adopted for MANs called Distributed Queue Dual Bus (DQDB) and is defined by IEEE 802.6. DQDB uses optical fibre in a dual-bus topology. Each bus has a head-end that initiates transmission activity. In the diagram below, traffic destined for a computer to the right of the source computer uses bus A, while traffic intended for a computer to the left uses bus B. Traffic on each bus is unidirectional, providing a fault-tolerant configuration. Bandwidth is allocated using time slots, and both synchronous and asynchronous modes are supported.
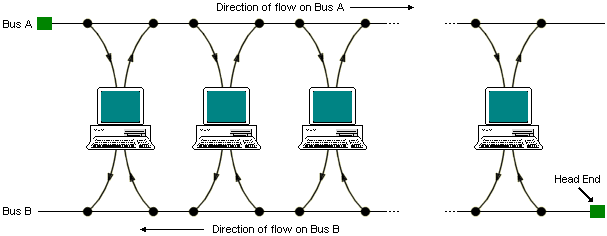
DQDB metropolitan area network architecture
