Circuit Switching
Circuit switching is a technique traditionally used in telephone networks to set up a connection between two subscribers. When two end-systems in a telecommunications network wish to communicate in this way, a dedicated circuit must be established between the two end points by allocating the required network resources prior to data transfer. The circuit remains in place until all the data has been transferred, and provides a fixed connection bandwidth.
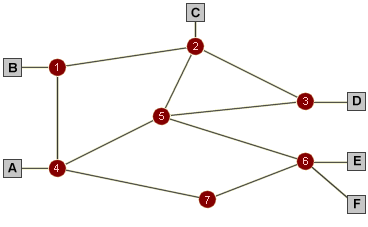
A generic switching network
Using the diagram above as an example, if station A has some data to send to station E, it sends a request to switching node 4 to establish a connection with station E. Node 4 must identify the optimum route based on currently available routing information. Assuming that node 5 is chosen as the next hop, node 4 will secure the first available channel link to node 5 for the connection. Node 5 will similarly reserve a channel link to node 6, which will then communicate with station E to establish whether station E want to accept the connection. If so, station A will receive a signal confirming that the connection has been established.
Once data transfer is complete, the connection is terminated by station A. Signals are sent to each of the nodes involved instructing them to de-allocate the network resources, which are then available for use in other connections. Circuit switching may be considered to be inefficient, because the entire capacity of the channels allocated to the circuit are unavailable for use in other circuits for the duration of the connection, even if no data is actually being sent, and the circuit may be idle for much of the time. There is also a delay involved in setting up the connection in the first place.
The diagram below shows the flow of information involved in setting up, using, and terminating the typical circuit-switched connection described above. Information orginating from station A is shown in pink, and information from station E is shown in blue.
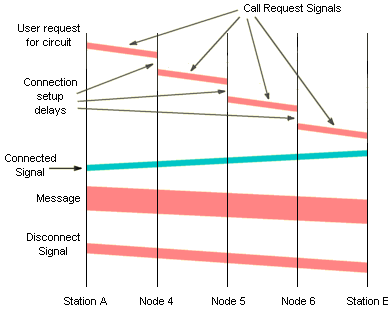
A circuit-switched connection
